Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 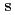 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 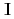 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 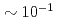 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (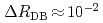 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Hosoma, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2016-019, 53 Pages, 2017/01
Application of probability generating function for nondestructive nuclear materials assay system was studied. First, high-order neutron correlations were derived algebraically up to septuplet and basic characteristics of the correlations were investigated. It was found that higher-order correlation increases rapidly in response to the increase of leakage multiplication, crosses and leaves lower-order correlations behind, when leakage multiplication is  1.3 that depends on detector efficiency and counter setting. Next, fission rates and doubles count rates by fast neutron and by thermal neutron in their coexisting system were derived algebraically. It was found that the number of induced fissions per unit time by fast neutron and by thermal neutron, the number of induced fissions (
1.3 that depends on detector efficiency and counter setting. Next, fission rates and doubles count rates by fast neutron and by thermal neutron in their coexisting system were derived algebraically. It was found that the number of induced fissions per unit time by fast neutron and by thermal neutron, the number of induced fissions ( 1) by one source neutron, and individual doubles count rates were possible to be estimated from Rossi-alpha combined distribution and measured ratio of each area obtained by differential die-away self-interrogation and conventional assay data.
1) by one source neutron, and individual doubles count rates were possible to be estimated from Rossi-alpha combined distribution and measured ratio of each area obtained by differential die-away self-interrogation and conventional assay data.
 B
B O
O crystal
crystalNakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Chen, Y. E.*; Ukibe, Masahiro*; Okubo, Masataka*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 559(2), p.766 - 768, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have been developing a position-sensitive neutron detector, which exhibits a high spatial resolution of the order of 10 microns and high detection efficiency. The analysis on the pulse-heights or on the time-delay between the STJs gives incident positions of the neutrons. In this paper, the response of the STJs/LBO neutron detector measured using a cold neutron beam is presented. The two STJs have the same size of 50  50
50  m
m and their distance is 1.3 mm. The count intensity in the correlation map varied depending on the incident position of the neutron beam which gives an evidence for the position-sensitivity of the detector. These experimental results were qualitatively understood by a simple solid-angle model.
and their distance is 1.3 mm. The count intensity in the correlation map varied depending on the incident position of the neutron beam which gives an evidence for the position-sensitivity of the detector. These experimental results were qualitatively understood by a simple solid-angle model.
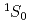 proton superfluidity in neutron star matter; Impact of bulk properties
proton superfluidity in neutron star matter; Impact of bulk propertiesTanigawa, Tomonori; Matsuzaki, Masayuki*; Chiba, Satoshi
Physical Review C, 70(6), p.065801_1 - 065801_7, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.36(Physics, Nuclear)We study the 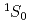 proton pairing gap in neutron star matterputting emphasis on influence of the Dirac effective mass and theproton fraction on the gap within the relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubovmodel. The gap equation is solved using the Bonn-B potential as aparticle-particle channel interaction. It is found that the maximalpairing gap
proton pairing gap in neutron star matterputting emphasis on influence of the Dirac effective mass and theproton fraction on the gap within the relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubovmodel. The gap equation is solved using the Bonn-B potential as aparticle-particle channel interaction. It is found that the maximalpairing gap 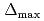 is 1-2MeV, which has a strongcorrelation with the Dirac effective mass. Hence we suggest that itserves as a guide to narrow down parameter sets of the relativisticeffective field theory. Furthermore, the more slowly protons increasewith density, the lower the peak of the gap and the wider thesuperfluid range become.
is 1-2MeV, which has a strongcorrelation with the Dirac effective mass. Hence we suggest that itserves as a guide to narrow down parameter sets of the relativisticeffective field theory. Furthermore, the more slowly protons increasewith density, the lower the peak of the gap and the wider thesuperfluid range become.
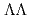 pairing and its dependence on background density in a relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov model
pairing and its dependence on background density in a relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov modelTanigawa, Tomonori; Matsuzaki, Masayuki*; Chiba, Satoshi
Physical Review C, 68(1), p.015801_1 - 015801_8, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.41(Physics, Nuclear)We calculate a 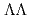 pairing gap in binary mixed matter of nucleons and
pairing gap in binary mixed matter of nucleons and  hyperons within the relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov model since a recent experiment suggests a weaker
hyperons within the relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov model since a recent experiment suggests a weaker 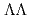 attraction than before, which has a significant impact on properties of neutron stars in various aspects. Lambda hyperons to be paired up are immersed in background nucleons in normal state. A phenomenological
attraction than before, which has a significant impact on properties of neutron stars in various aspects. Lambda hyperons to be paired up are immersed in background nucleons in normal state. A phenomenological 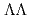 interaction, which is derived relativistically from the Lagrangian of the system, is adopted to the gap equation. It is found that at background density
interaction, which is derived relativistically from the Lagrangian of the system, is adopted to the gap equation. It is found that at background density 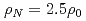 the
the 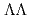 pairing gap is very small, and that denser background makes it rapidly suppressed. This result suggests a mechanism, specific to mixed matter dealt with relativistic models, of its dependence on the nucleon density.
pairing gap is very small, and that denser background makes it rapidly suppressed. This result suggests a mechanism, specific to mixed matter dealt with relativistic models, of its dependence on the nucleon density.
Okajima, Shigeaki; Yamane, Yoshihiro*; Takemoto, Yoshinari*; Sakurai, Takeshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 37(8), p.720 - 723, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; *; *; *; *; *; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Fujine, Shigenori*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 377, p.148 - 152, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
;
Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement, (69), p.406 - 419, 1980/00
no abstracts in English